Introduction to the Mevspace DNS
DNS - Foundation that drive the Internet
DNS (Domain Name System) is one of the most essential factor that allows us to navigate the Internet in an easy and intuitive way. It acts like a virtual translator that converts user-friendly Internet addresses, such as www.example.com, into IP numbers, such as 192.192.192.192, that computers and servers can understand. Without DNS, the entire Internet would base itself on memorizing complex, numerical strings of addresses. DNS is what makes the Internet accessible to everyone.
How does DNS work?
Managing Mevspace's DNS function
To improve the management of network connections and provide faster access to resources on the Internet, we offer to all our clients a free DNS service - convenient, fast and easy to set up. See how to do it in a few simple steps.
Creating a new domain
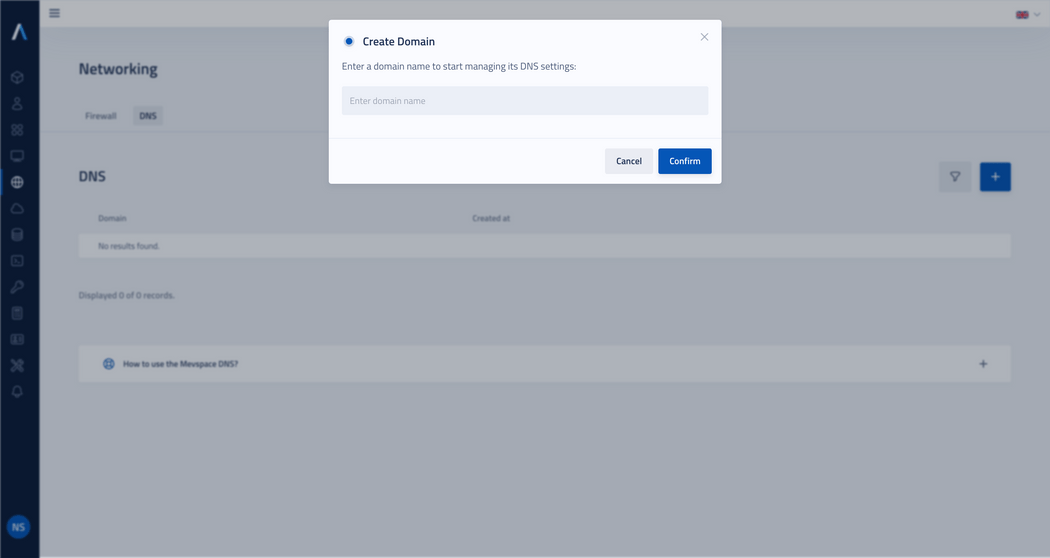
Click on the plus icon to create a new domain.
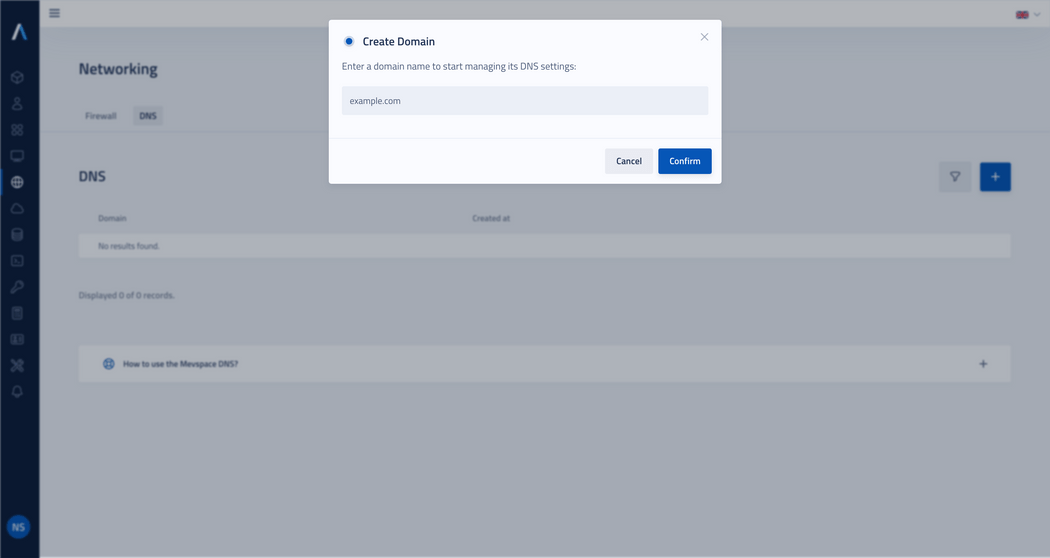
Enter the domain name and click Confirm.
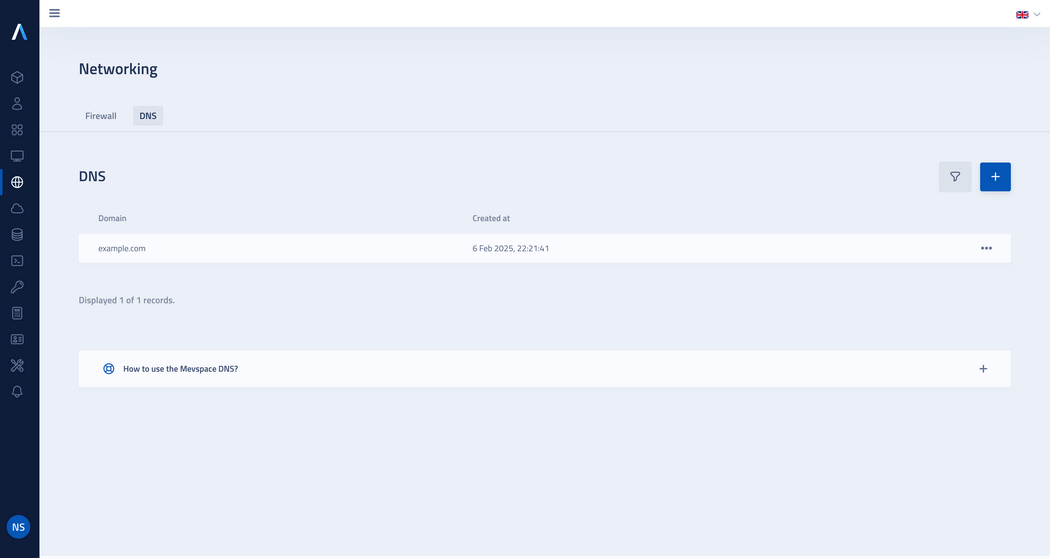
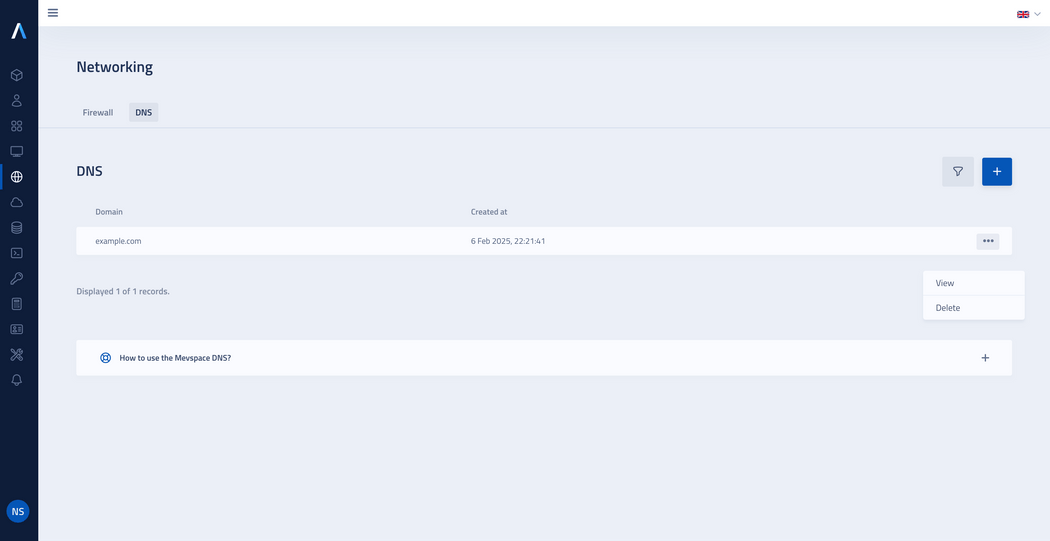
Displaying created domains
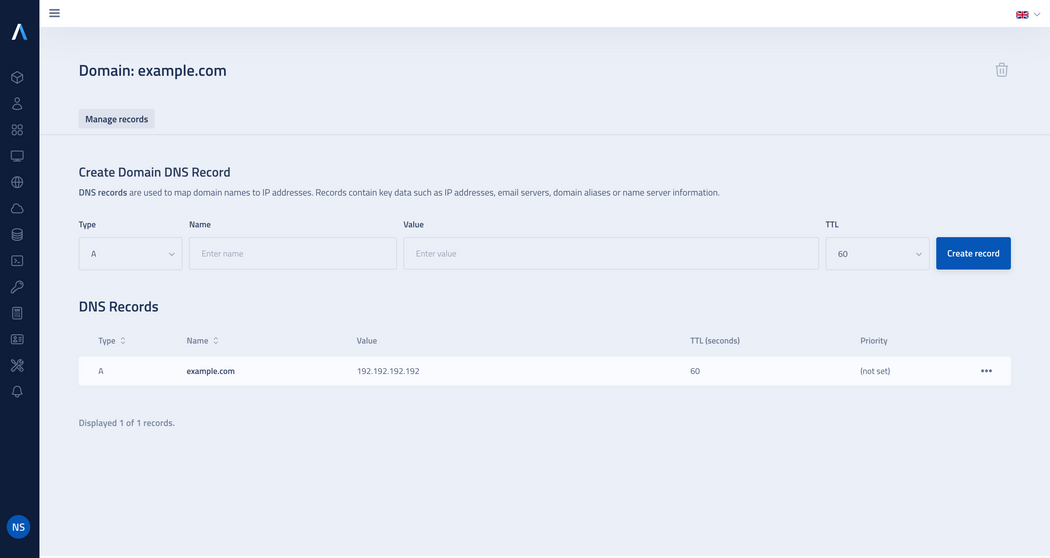
Once the domain is created, you will see new entry in the list.
Click on domain name or use the action button by selecting View from the drop-down menu to access the DNS records management view.
DNS records management view
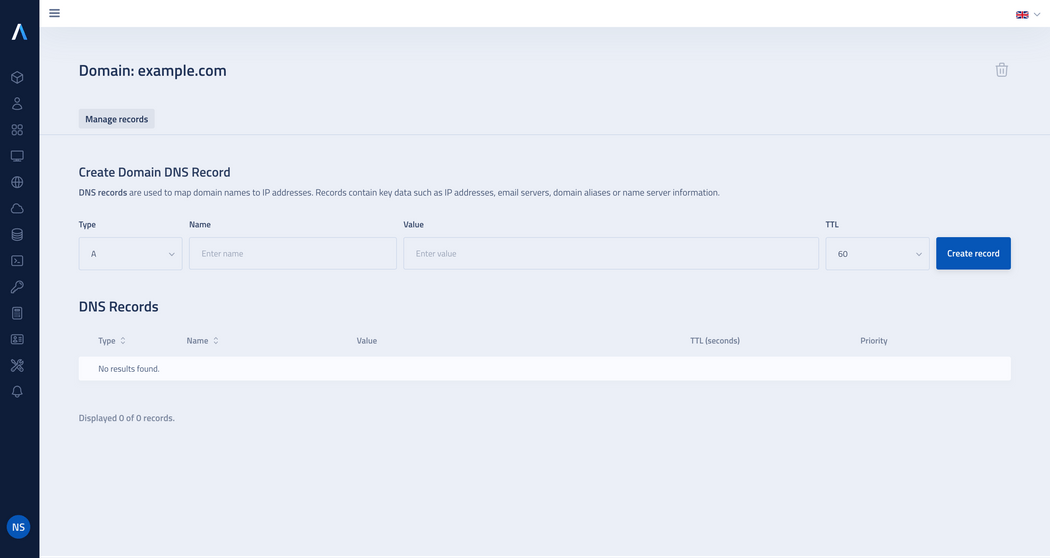
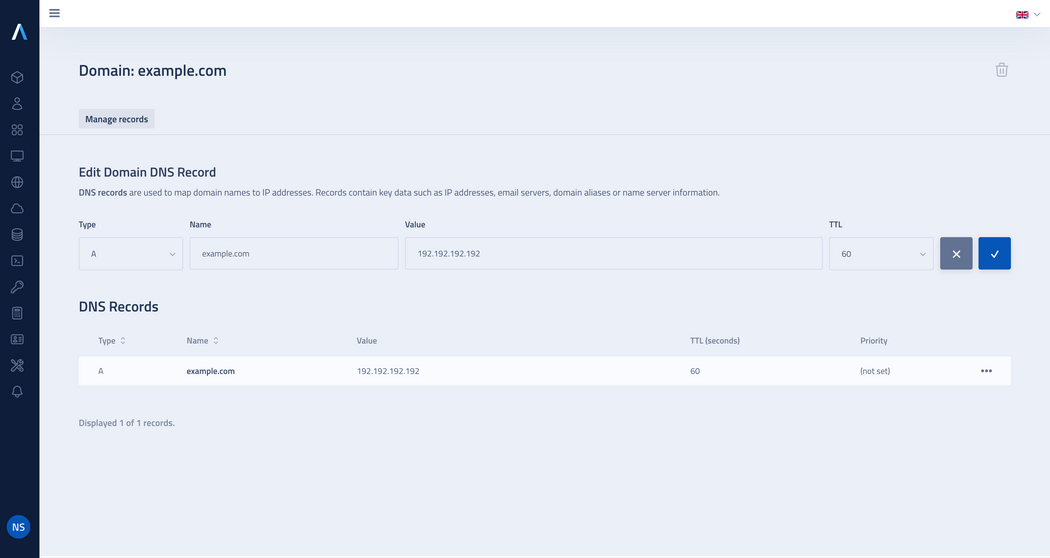
In the domain detail view you will find a form for adding DNS records.
From this level, you can perform additional operations, such as editing and deleting record and deleting the entire DNS zone.
DNS record creation
In the Create Domain DNS record form, configure all the required parameters:
Type: Select one from the available types of records: A, AAAA, CNAME, NS, MX, SRV or TXT.
Name: Enter name of the DNS record.
Value: Enter value of the record.
TTL: Specify amount of time (in seconds) for which the DNS record will be cached on the DNS server.
Priority (for MX and SRV records): Specify priority of the mail server.
Weight (for SRV records): Specify preference of servers providing the same service - the higher the value, the higher the priority when establishing a connection.
Port (for SRV records): Specify port number on which the service operates.
After configuring your record, click on the Create button.
Note: The DNS addresses to which you must redirect your domain are: ns1.mevnode.com and ns2.mevnode.com. Note that some domain providers require you to first create a DNS zone before performing delegation.
DNS record types
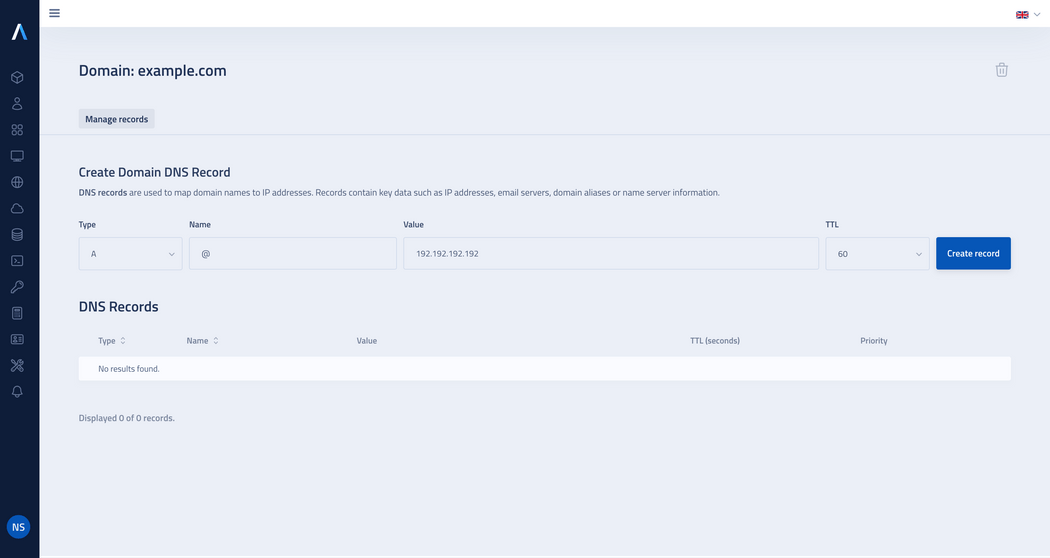
A (Address record)
The A record is used to map a domain name to a corresponding IPv4 address.
Example:
For the Name field:
Enter @ to refer record to the main domain name
Enter the full domain name, e.g. test.pl
Enter a subdomain name, e.g. waw, which will refer record to waw.test.pl
For the Value field: Enter the IPv4 address.
For the TTL field: A shorter TTL time ensures that changes to DNS records are propagated faster, but it results in more requests. If the IP address is static, it's a useful to set the TTL to 60 seconds to ensure users get regular updates. By default, the TTL is 60 seconds.
AAAA (IPv6 Address Record)
The AAAA record is used to map a domain name to a corresponding IPv6 address.
Example:
For the Name field:
Enter @ to refer record to the main domain name
Enter the full domain name, e.g. test.pl
Enter a subdomain name, e.g. waw, which will refer record to waw.test.pl
For the Value field: Enter the IPv6 address.
For the TTL field: A shorter TTL time ensures that changes to DNS records are propagated faster, but it results in more requests. If the IP address is static, it's a useful to set the TTL to 60 seconds to ensure users get regular updates. By default, the TTL is 60 seconds.
CNAME (Canonical Name Record)
The CNAME record is used to create aliases for domains that direct DNS requests to other records, such as A or AAAA, allowing traffic to be redirected between domains.
Example:
For the Name field:
Enter @ to refer record to the main domain name
Enter the full domain name, e.g. test.pl
Enter a subdomain name, e.g. blog, which will refer record to blog.test.pl
For the Value field: Enter name of the target domain.
For the TTL field: A shorter TTL time ensures that changes to DNS records are propagated faster, but it results in more requests. If the IP address is static, it's a useful to set the TTL to 60 seconds to ensure users get regular updates. By default, the TTL is 60 seconds.
NS (Name Server Record)
The NS record is used to define name servers that are responsible for handling a specific rule.
Example:
For the Name field:
Enter @ to refer record to the main domain name
Enter the full domain name, e.g. test.pl
Enter a subdomain name, e.g. waw, which will refer record to waw.test.pl
For the Value field: Enter name of the target domain.
For the TTL field: A shorter TTL time ensures that changes to DNS records are propagated faster, but it results in more requests. If the IP address is static, it's a useful to set the TTL to 60 seconds to ensure users get regular updates. By default, the TTL is 60 seconds.
MX (Mail Exchange Record)
The MX record is used to route email traffic for a given domain.
Example:
For the Name field:
Enter @ to refer record to the main domain name
Enter the full domain name, e.g. test.pl
Enter a subdomain name, e.g. waw, which will refer record to waw.test.pl
For the Value field: Enter name of the target domain.
For the Priority field: Enter a number. A lower value indicates a higher priority.
For the TTL field: A shorter TTL time ensures that changes to DNS records are propagated faster, but it results in more requests. If the IP address is static, it's a useful to set the TTL to 60 seconds to ensure users get regular updates. By default, the TTL is 60 seconds.
SRV (Service Locator)
The SRV record is used to identify services available in a domain.
Example:
For the Name field:
Enter @ to refer record to the main domain name
Enter the full domain name, e.g. test.pl
Enter a subdomain name, e.g. waw, which will refer record to waw.test.pl
For the Value field: Enter name of the target domain.
For the Priority field: Enter a number. A lower value indicates a higher priority.
For the Weight field: Enter the server weight, which determines how often requests will be directed to this server compared to others. A higher weight means a higher number of requests.
For the Port field: Enter port number on which the service operates.
For the TTL field: A shorter TTL time ensures that changes to DNS records are propagated faster, but it results in more requests. If the IP address is static, it's a useful to set the TTL to 60 seconds to ensure users get regular updates. By default, the TTL is 60 seconds.
TXT (Text Record)
The TXT record contains any text, used to store descriptive information about the domain.
Example:
For the Name field:
Enter @ to refer record to the main domain name
Enter the full domain name, e.g. test.pl
Enter a subdomain name, e.g. waw, which will refer record to waw.test.pl
For the Value field: Enter any string you want to store in the TXT record. This can be informational text, verification data, configuration settings or any other value you want to associate with the domain.
For the TTL field: A shorter TTL time ensures that changes to DNS records are propagated faster, but it results in more requests. If the IP address is static, it's a useful to set the TTL to 60 seconds to ensure users get regular updates. By default, the TTL is 60 seconds.
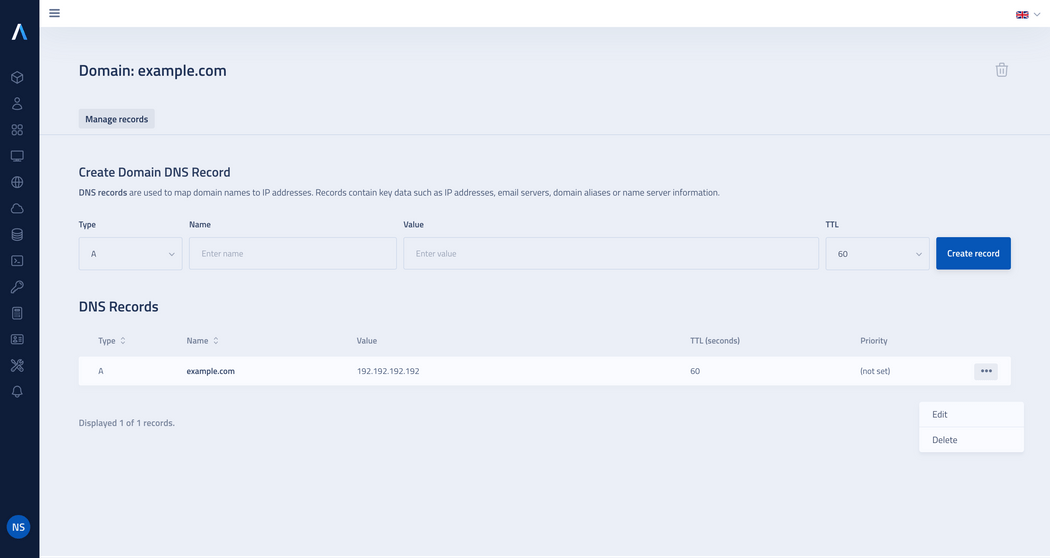
Editing and deleting a DNS record
- To edit a record, click the action button and select Edit from the drop-down list, if you need to delete the record, select Delete.
DNS zone deletion
To delete an entire DNS zone (a domain with its associated records), click the trash icon in the management view.
Alternatively, in the list of domains, click the action button and select Delete from the drop-down menu.